本文主要介绍Llama的模型结构和主要优化特性。
Model Architecture
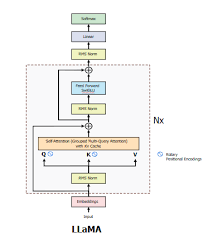
Llama结构整体如上,是个典型的decoder-only结构,它包含如下部分:
- Embedding
- Transformer stack
- RMS Norm
- Linear
- Softmax
Transformer stack包含多个Transformer block,每个block包含如下部分:
- RMS Norm
- Rotary positional Encoding
- Grouped Multi-Query Attention
- Add
- RMS Norm
- Feed Forward SwiGLU
与其他开源模型关系
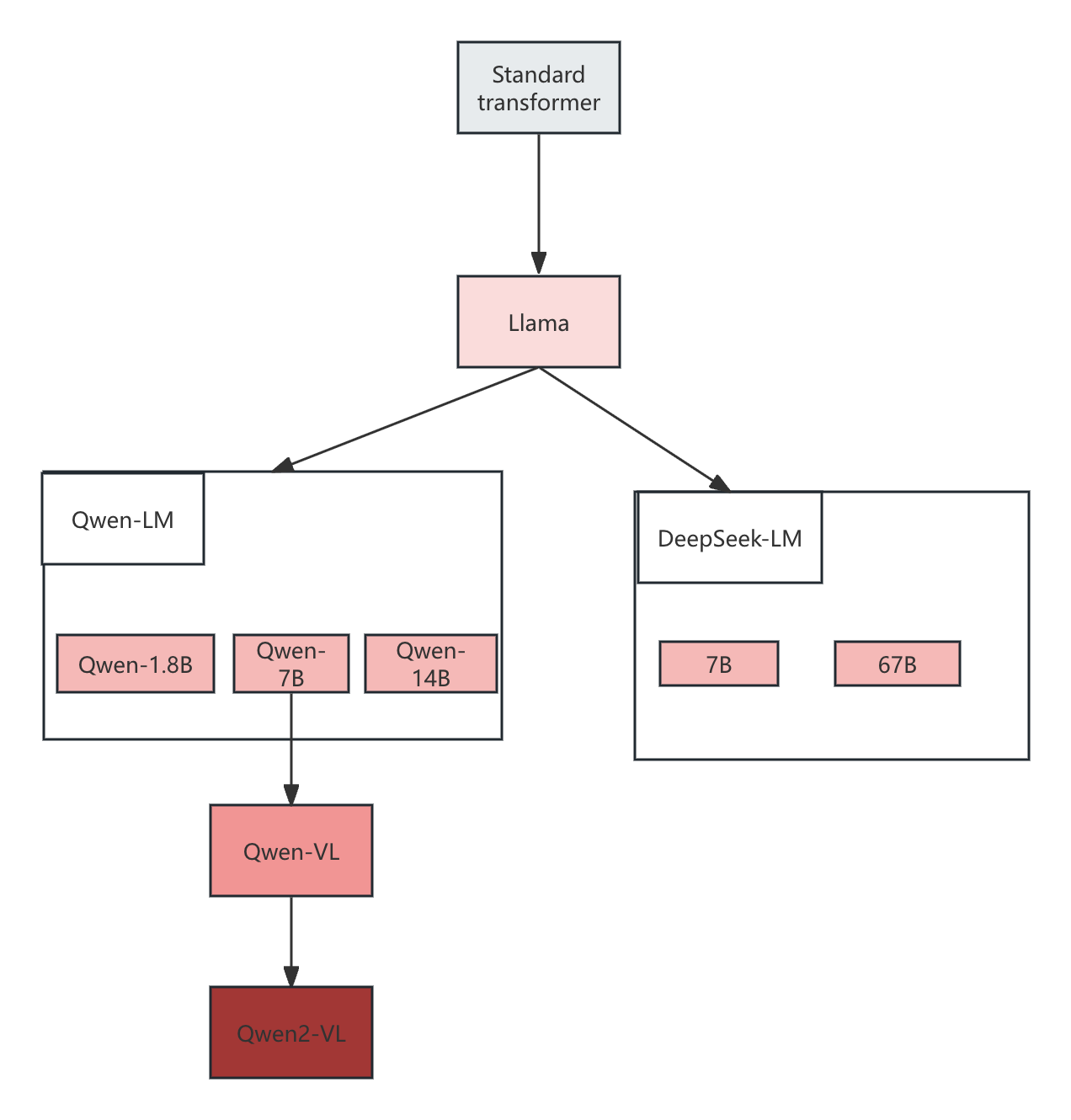
Qwen和DeepSeek都借鉴了Llama的结构
主要优化特性
RoPE
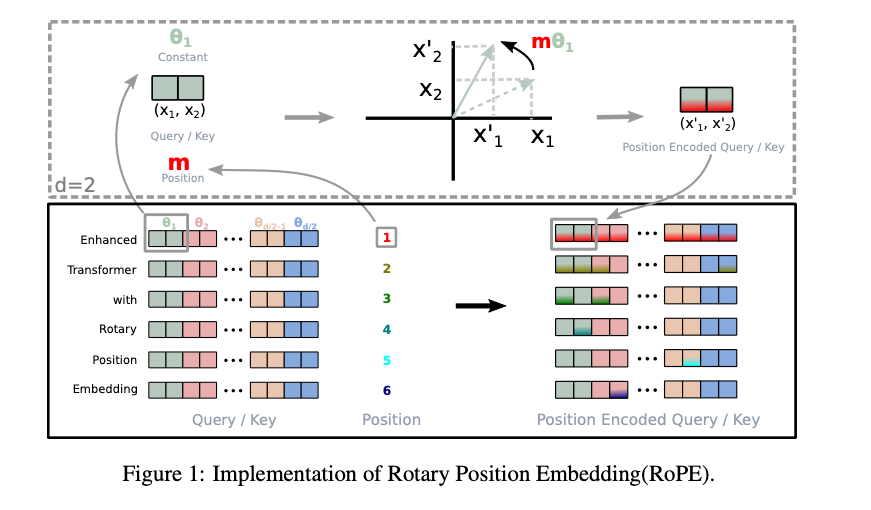
假设当前输入三个token,记为$x_1,x_2,x_3$,输出embedding维度为$2$
设$K$和$V$的线性投影矩阵为$W_k \in R^{2\times2}$,$W_q \in R^{2\times2}$,$W_v \in R^{2\times2}$
\[K = W_k \cdot X\\ Q = W_q \cdot X\\ V = W_v \cdot X\\ X \in R^{2\times3}\\ X=\begin{bmatrix} x_1; x_2; x_3 \end{bmatrix}\\\]我们当前的旋转编码矩阵
对于$x_2$为 \(R_{\theta,2}^2= \begin{bmatrix} \cos(\theta_2) & -\sin(\theta_2) \\ \sin(\theta_2) & \cos(\theta_2) \end{bmatrix}\)
编码后 \(R_{\theta,2}^2 \cdot W_k \cdot x_2\\ R_{\theta,2}^2 \cdot W_q \cdot x_2\)
注意是先线性投影再编码
对于$x_3$为 \(R_{\theta,3}^2= \begin{bmatrix} \cos(\theta_3) & -\sin(\theta_3) \\ \sin(\theta_3) & \cos(\theta_3) \end{bmatrix}\)
编码后 \(X_3=R_{\theta,3}^2 \cdot W_k \cdot x_3 \\ X_3=R_{\theta,3}^2 \cdot W_q \cdot x_3\)
那么当$K$与$Q$做点击积时$Q^TK$,对于$Q$的第二列与$K$的第三行 \((R_{\theta,2}^2W_qx_2)^T(R_{\theta,3}^2W_kx_3)=X_2^T W_q^T {R_{\theta,2}^{2\top} R_{\theta,3}^2} W_kx_3\)
\[R_{\theta,2}^{2\top} R_{\theta,3}^2 = \begin{pmatrix} \cos(\theta_2 - \theta_3) & -\sin(\theta_2 - \theta_3) \\ \sin(\theta_2 - \theta_3) & \cos(\theta_2 - \theta_3) \\ \end{pmatrix}\]如上所示,第2个和第3个token的相对位置信息被RoPE带入了进来
可以推广到高维情景,如下
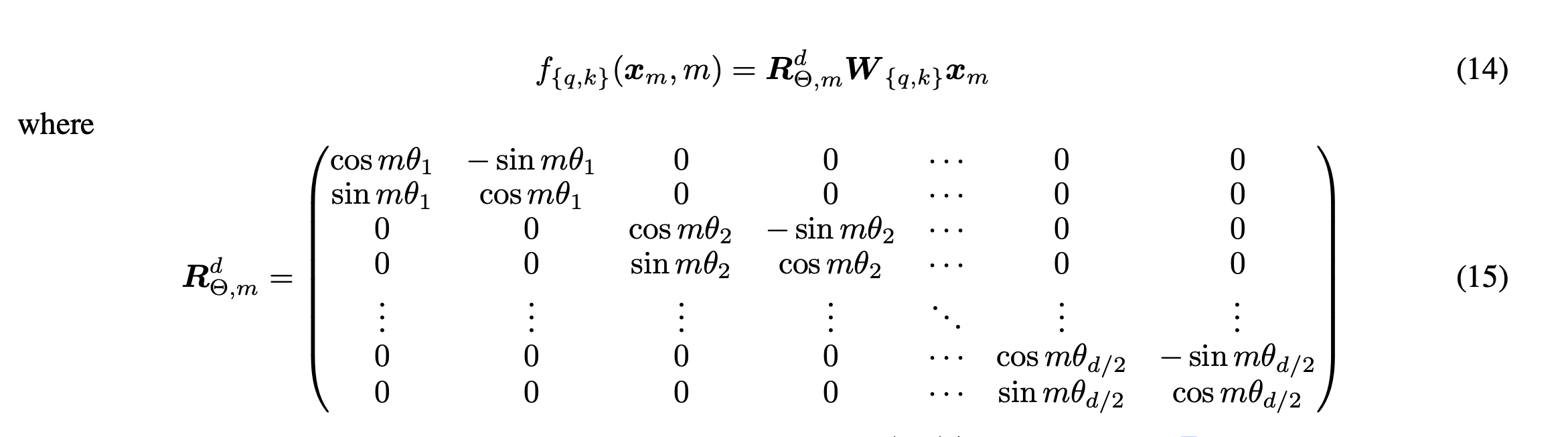
其中
\[R_{\theta,n-m}^d=(R_{\theta,m}^d)^TR_{\theta,n}^d\]Grouped Multi-Query Attention
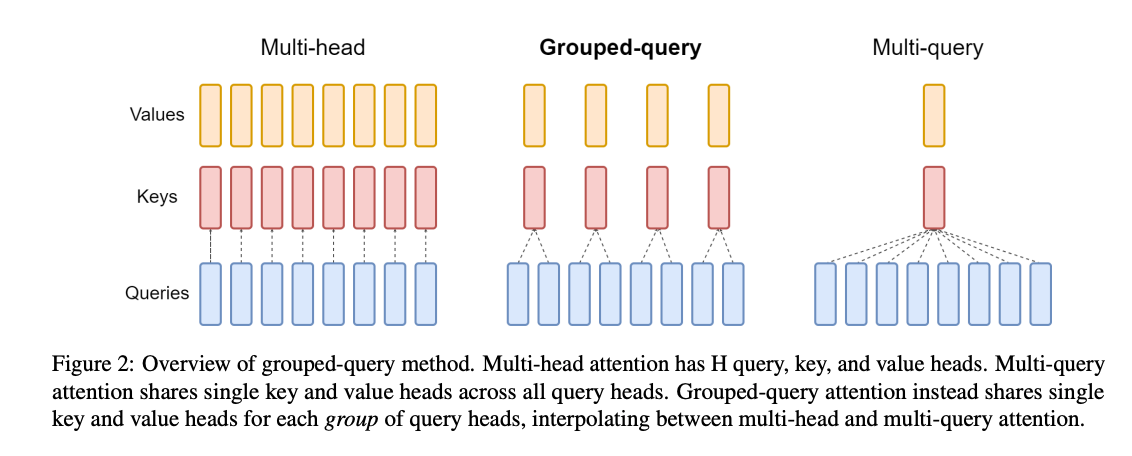
以输入100个token为例,token的embedding维度为512
注意力头数$h=8$,分组数$num_heads=2$
输入$X \in R^{100 \times 512}$,$8$个注意力头划分为$2$个组
\[Q = XW^Q, W^Q \in R^{512\times512}\\ K = XW^K, W^K \in R^{512\times128}\\ V = XW^V, W^V \in R^{512\times128}\]此时的$Q \in R^{100 \times 512}$,$K \in R^{100 \times 128}$,$V \in R^{100 \times 128}$
每个注意力头的维度为64,每组k和v的维度为64且被组内4个注意力头共享
注意力计算公式如下
\[head_i=softmax(\frac{Q_iK_g^T}{\sqrt{d_k}})V_g\\ Q_i \in R^{100\times64} , 1<=i<=8\\ K_g \in R^{100\times64} , 1<=g<=2\\ V_g \in R^{100\times64} , 1<=g<=2\\\]这里的$K_g$和$V_g$对于$Q_i,Q_{i+1},Q_{i+2},Q_{i+3}$是一样的
最后再将注意力头拼接,映射回模型维度大小,因此$Y \in R^{100\times512}$ \(Y=GQA(X)=Concat(head_1,head_2,...,head_8)W^O\\ W^O \in R^{512\times512}\)
小结
从上面的计算过程分析可知:
- 注意力头的计算量并没有减少,但是计算$K$和$V$的线性投影矩阵大小和计算量都发生了变化
- 需要存储的$K$和$V$大小发生了变化,缩小$\frac{h}{num_groups}$倍
实践中,GQA只应用到decoder层,不应用到encoder层,因为encoder层的token输入不会在后续发生变化;decoder因为输入会逐渐增大,进而需要缓存越来越多的KV数据。